stouputils.ctx module#
This module provides context managers for temporarily silencing output.
Muffle: Context manager that temporarily silences output (alternative to stouputils.decorators.silent())
LogToFile: Context manager to log to a file every print call (with LINE_UP handling)
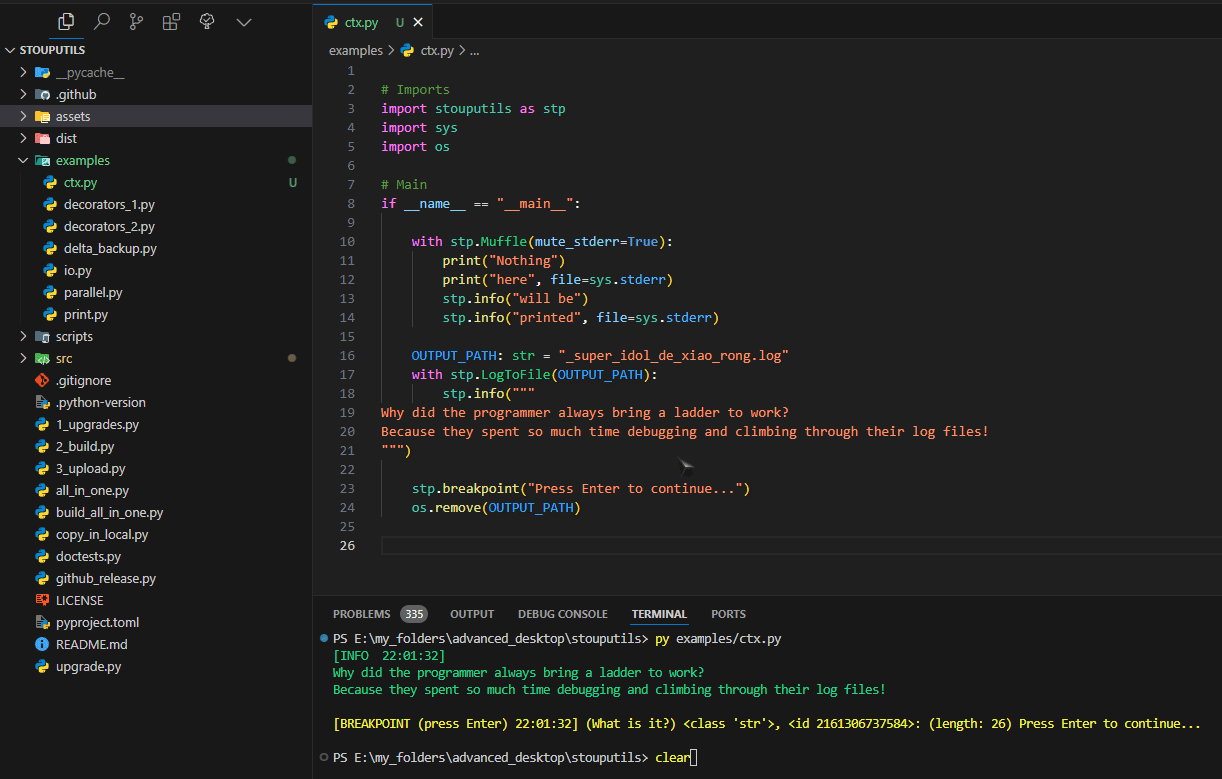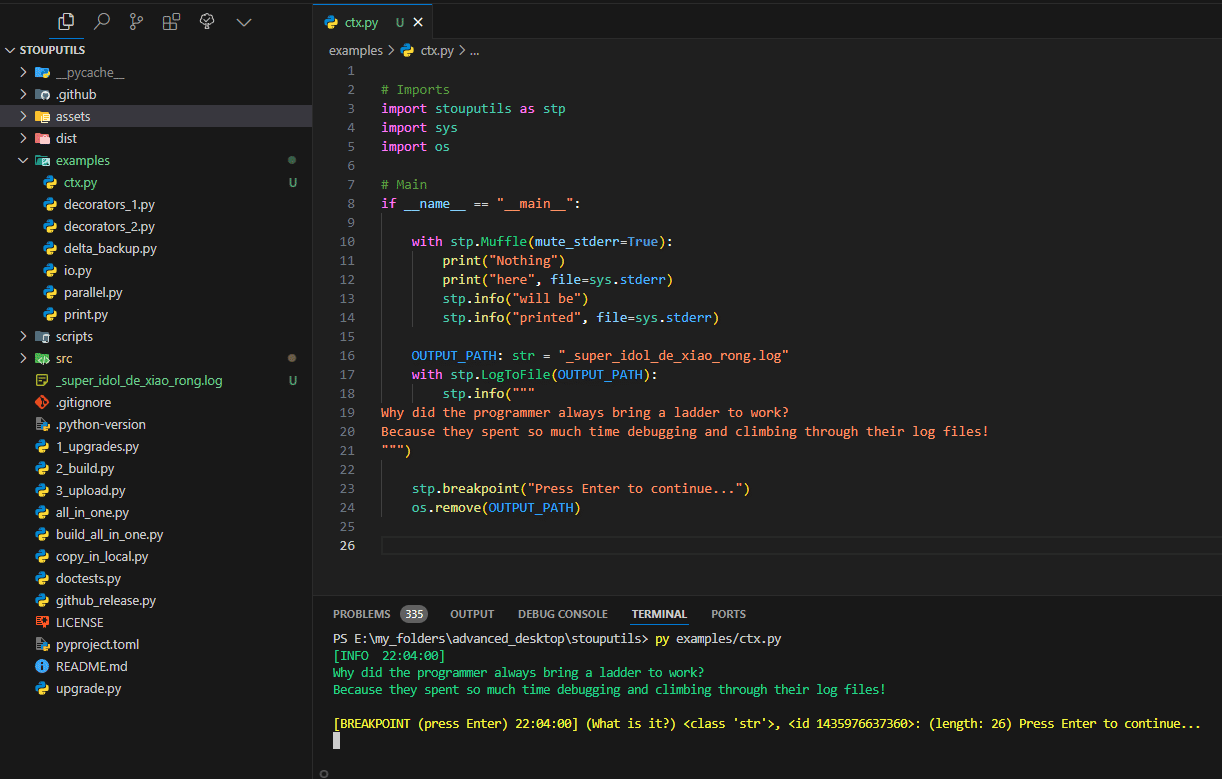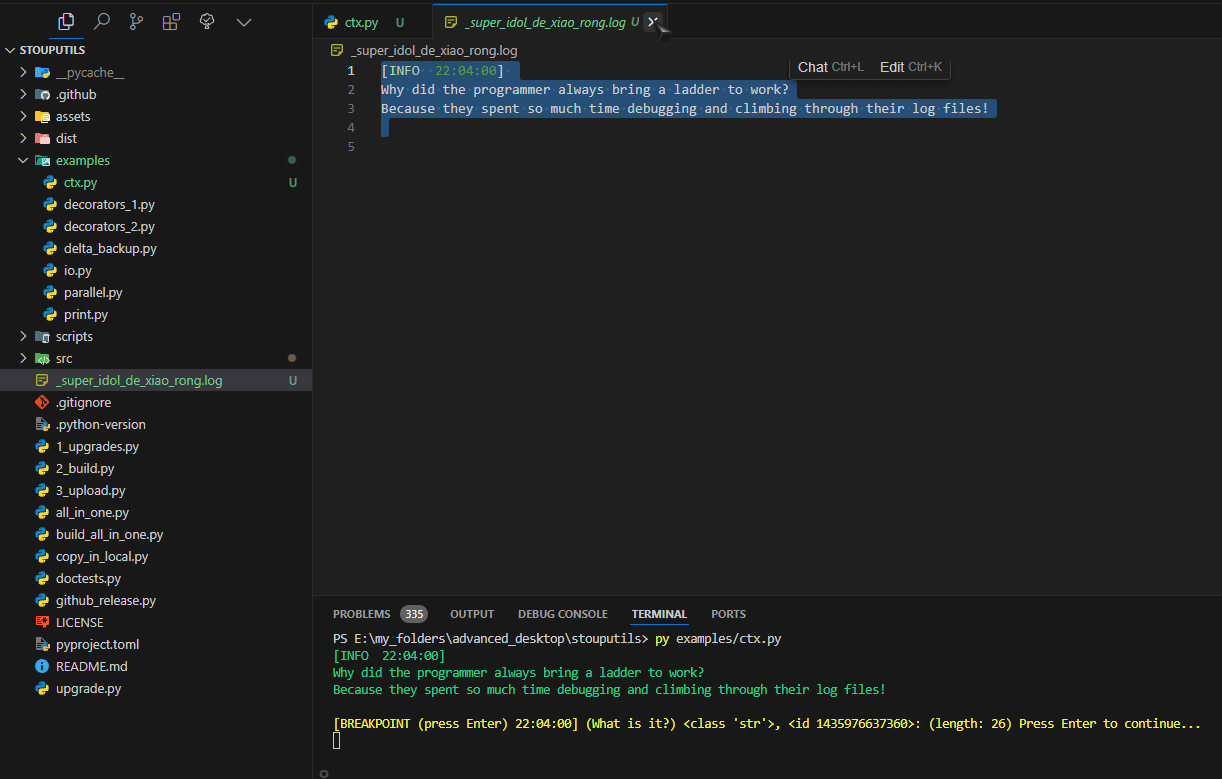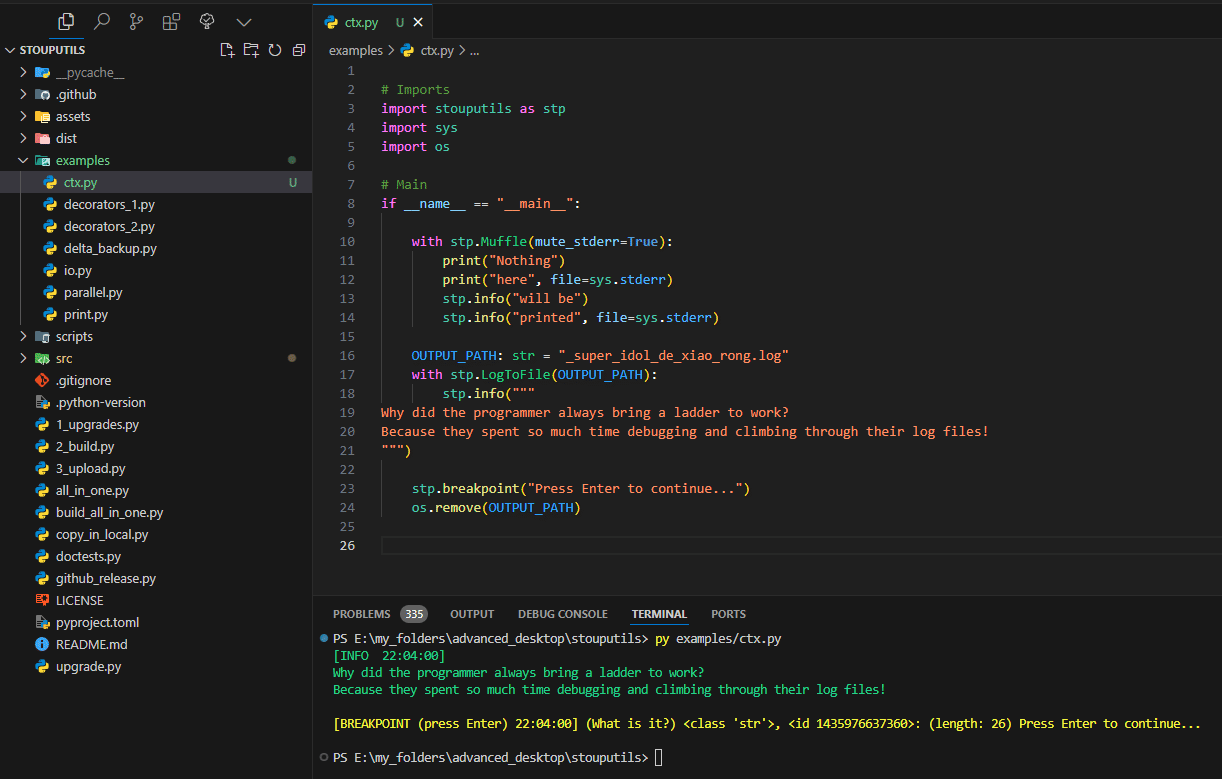
- class Muffle(mute_stderr: bool = False)[source]#
Bases:
objectContext manager that temporarily silences output.
Alternative to stouputils.decorators.silent()
Examples
>>> with Muffle(): ... print("This will not be printed")
- mute_stderr: bool#
Attribute remembering if stderr should be muted
- original_stdout: TextIO#
Attribute remembering original stdout
- original_stderr: TextIO#
Attribute remembering original stderr
- class LogToFile(path: str, mode: str = 'w', encoding: str = 'utf-8', tee_stdout: bool = True, tee_stderr: bool = True, ignore_lineup: bool = True)[source]#
Bases:
objectContext manager to log to a file.
This context manager allows you to temporarily log output to a file while still printing normally. The file will receive log messages without ANSI color codes.
- Parameters:
path (str) – Path to the log file
mode (str) – Mode to open the file in (default: “w”)
encoding (str) – Encoding to use for the file (default: “utf-8”)
tee_stdout (bool) – Whether to redirect stdout to the file (default: True)
tee_stderr (bool) – Whether to redirect stderr to the file (default: True)
ignore_lineup (bool) – Whether to ignore lines containing LINE_UP escape sequence in files (default: False)
Examples
> import stouputils as stp > with stp.LogToFile("output.log"): > stp.info("This will be logged to output.log and printed normally") > print("This will also be logged")
- path: str#
Attribute remembering path to the log file
- mode: str#
Attribute remembering mode to open the file in
- encoding: str#
Attribute remembering encoding to use for the file
- tee_stdout: bool#
Whether to redirect stdout to the file
- tee_stderr: bool#
Whether to redirect stderr to the file
- ignore_lineup: bool#
Whether to ignore lines containing LINE_UP escape sequence in files
- file: IO[Any]#
Attribute remembering opened file
- original_stdout: TextIO#
Original stdout before redirection
- original_stderr: TextIO#
Original stderr before redirection
- static common(logs_folder: str, filepath: str, func: Callable[[...], Any], *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) Any[source]#
Common code used at the beginning of a program to launch main function
- Parameters:
logs_folder (str) – Folder to store logs in
filepath (str) – Path to the main function
func (Callable[..., Any]) – Main function to launch
*args (tuple[Any, ...]) – Arguments to pass to the main function
**kwargs (dict[str, Any]) – Keyword arguments to pass to the main function
- Returns:
Return value of the main function
- Return type:
Any
Examples
>>> if __name__ == "__main__": ... LogToFile.common(f"{ROOT}/logs", __file__, main)
- class MeasureTime(print_func: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], None] = <function debug>, message: str = 'Execution time', perf_counter: bool = True)[source]#
Bases:
objectContext manager to measure execution time.
This context manager measures the execution time of the code block it wraps and prints the result using a specified print function.
- Parameters:
print_func (Callable) – Function to use to print the execution time (e.g. debug, info, warning, error, etc.).
message (str) – Message to display with the execution time. Defaults to “Execution time”.
perf_counter (bool) – Whether to use time.perf_counter_ns or time.time_ns. Defaults to True.
Examples
> import time > import stouputils as stp > with stp.MeasureTime(stp.info, message="My operation"): ... time.sleep(0.5) > # [INFO HH:MM:SS] My operation: 500.123ms (500123456ns) > with stp.MeasureTime(): # Uses debug by default ... time.sleep(0.1) > # [DEBUG HH:MM:SS] Execution time: 100.456ms (100456789ns)
- print_func: Callable[[...], None]#
Function to use for printing the execution time
- message: str#
Message to display with the execution time
- perf_counter: bool#
Whether to use time.perf_counter_ns or time.time_ns
- ns: Callable[[], int]#
Time function to use
- start_ns: int#
Start time in nanoseconds