stouputils.collections module#
This module provides utilities for collection manipulation:
unique_list: Remove duplicates from a list while preserving order using object id, hash or str
at_least_n: Check if at least n elements in an iterable satisfy a given predicate
sort_dict_keys: Sort dictionary keys using a given order list (ascending or descending)
upsert_in_dataframe: Insert or update a row in a Polars DataFrame based on primary keys
array_to_disk: Easily handle large numpy arrays on disk using zarr for efficient storage and access.
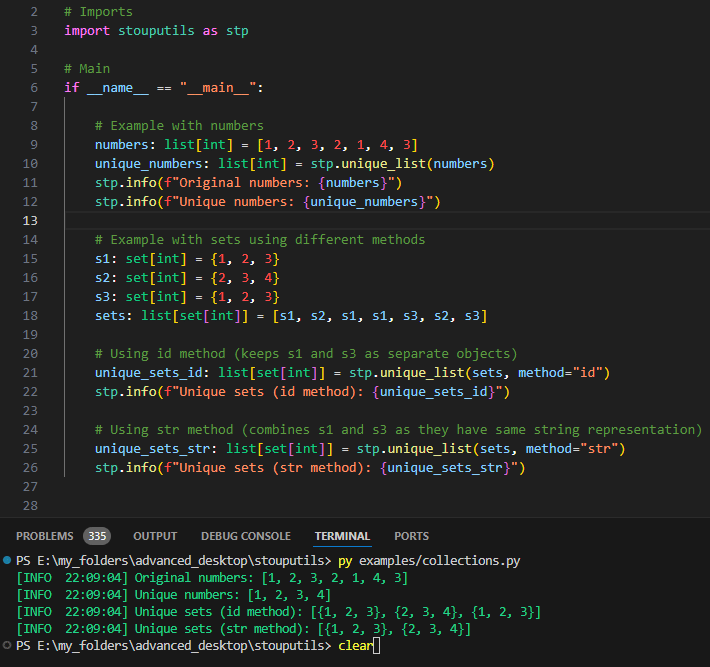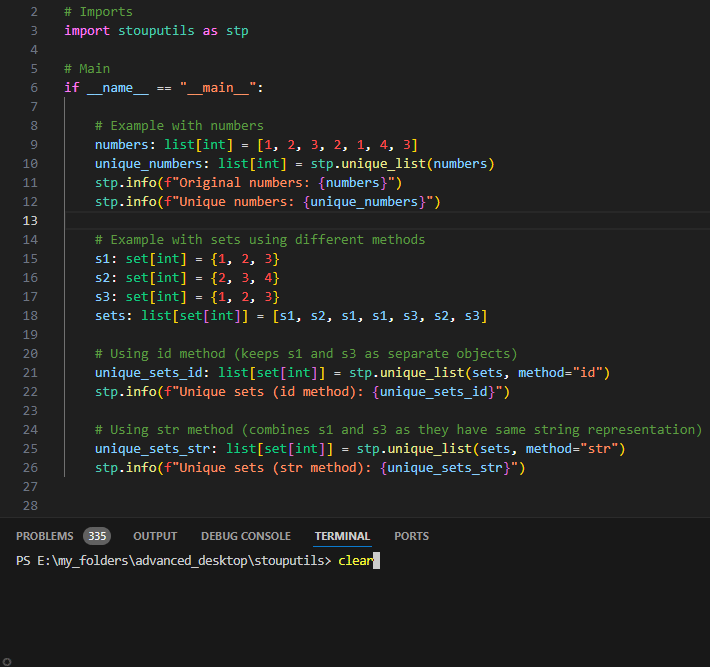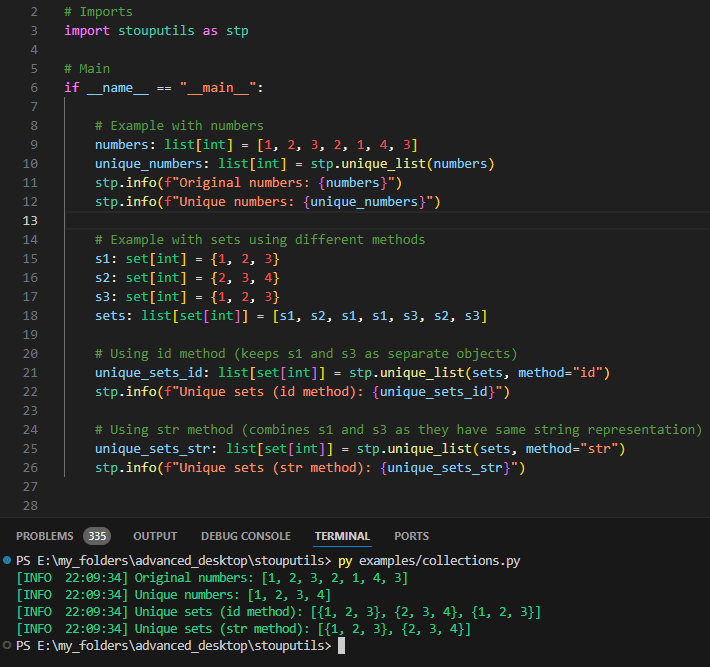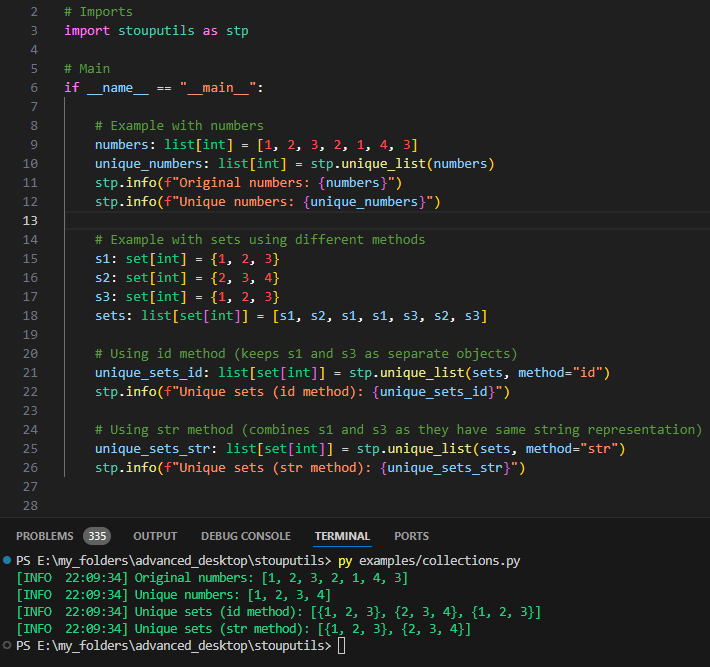
- unique_list(
- list_to_clean: Iterable,
- method: Literal['id', 'hash', 'str'] = 'str',
Remove duplicates from the list while keeping the order using ids, hash, or str
- Parameters:
list_to_clean (Iterable[T]) – The list to clean
method (Literal["id", "hash", "str"]) – The method to use to identify duplicates
- Returns:
The cleaned list
- Return type:
list[T]
Examples
>>> unique_list([1, 2, 3, 2, 1], method="id") [1, 2, 3]
>>> s1 = {1, 2, 3} >>> s2 = {2, 3, 4} >>> s3 = {1, 2, 3} >>> unique_list([s1, s2, s1, s1, s3, s2, s3], method="id") [{1, 2, 3}, {2, 3, 4}, {1, 2, 3}]
>>> s1 = {1, 2, 3} >>> s2 = {2, 3, 4} >>> s3 = {1, 2, 3} >>> unique_list([s1, s2, s1, s1, s3, s2, s3], method="str") [{1, 2, 3}, {2, 3, 4}]
- at_least_n(
- iterable: Iterable,
- predicate: Callable[[T], bool],
- n: int,
Return True if at least n elements in iterable satisfy predicate. It’s like the built-in any() but for at least n matches.
Stops iterating as soon as n matches are found (short-circuit evaluation).
- Parameters:
iterable (Iterable[T]) – The iterable to check.
predicate (Callable[[T], bool]) – The predicate to apply to items.
n (int) – Minimum number of matches required.
- Returns:
True if at least n elements satisfy predicate, otherwise False.
- Return type:
bool
Examples
>>> at_least_n([1, 2, 3, 4, *[i for i in range(5, int(1e5))]], lambda x: x % 2 == 0, 2) True >>> at_least_n([1, 3, 5, 7], lambda x: x % 2 == 0, 1) False
- sort_dict_keys(
- dictionary: dict[T, Any],
- order: list[T],
- reverse: bool = False,
Sort dictionary keys using a given order list (reverse optional)
- Parameters:
dictionary (dict[T, Any]) – The dictionary to sort
order (list[T]) – The order list
reverse (bool) – Whether to sort in reverse order (given to sorted function which behaves differently than order.reverse())
- Returns:
The sorted dictionary
- Return type:
dict[T, Any]
Examples
>>> sort_dict_keys({'b': 2, 'a': 1, 'c': 3}, order=["a", "b", "c"]) {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
>>> sort_dict_keys({'b': 2, 'a': 1, 'c': 3}, order=["a", "b", "c"], reverse=True) {'c': 3, 'b': 2, 'a': 1}
>>> sort_dict_keys({'b': 2, 'a': 1, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}, order=["c", "b"]) {'c': 3, 'b': 2, 'a': 1, 'd': 4}
- upsert_in_dataframe(
- df: pl.DataFrame,
- new_entry: dict[str, Any],
- primary_keys: list[str] | dict[str, Any] | None = None,
Insert or update a row in the Polars DataFrame based on primary keys.
- Parameters:
df (pl.DataFrame) – The Polars DataFrame to update.
new_entry (dict[str, Any]) – The new entry to insert or update.
primary_keys (list[str] | dict[str, Any] | None) – The primary keys to identify the row (for updates).
- Returns:
The updated Polars DataFrame.
- Return type:
pl.DataFrame
Examples
>>> import polars as pl >>> df = pl.DataFrame({"id": [1, 2], "value": ["a", "b"]}) >>> new_entry = {"id": 2, "value": "updated"} >>> updated_df = upsert_in_dataframe(df, new_entry, primary_keys=["id"]) >>> print(updated_df) shape: (2, 2) ┌─────┬─────────┐ │ id ┆ value │ │ --- ┆ --- │ │ i64 ┆ str │ ╞═════╪═════════╡ │ 1 ┆ a │ │ 2 ┆ updated │ └─────┴─────────┘
>>> new_entry = {"id": 3, "value": "new"} >>> updated_df = upsert_in_dataframe(updated_df, new_entry, primary_keys=["id"]) >>> print(updated_df) shape: (3, 2) ┌─────┬─────────┐ │ id ┆ value │ │ --- ┆ --- │ │ i64 ┆ str │ ╞═════╪═════════╡ │ 1 ┆ a │ │ 2 ┆ updated │ │ 3 ┆ new │ └─────┴─────────┘
- array_to_disk(
- data: NDArray[Any] | zarr.Array,
- delete_input: bool = True,
- more_data: NDArray[Any] | zarr.Array | None = None,
Easily handle large numpy arrays on disk using zarr for efficient storage and access.
Zarr provides a simpler and more efficient alternative to np.memmap with better compression and chunking capabilities.
- Parameters:
data (NDArray | zarr.Array) – The data to save/load as a zarr array
delete_input (bool) – Whether to delete the input data after creating the zarr array
more_data (NDArray | zarr.Array | None) – Additional data to append to the zarr array
- Returns:
The zarr array, the directory path, and the total size in bytes
- Return type:
tuple[zarr.Array, str, int]
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> data = np.random.rand(1000, 1000) >>> zarr_array = array_to_disk(data)[0] >>> zarr_array.shape (1000, 1000)
>>> more_data = np.random.rand(500, 1000) >>> longer_array, dir_path, total_size = array_to_disk(zarr_array, more_data=more_data)