stouputils.decorators module#
This module provides decorators for various purposes:
measure_time(): Measure the execution time of a function and print it with the given print function
handle_error(): Handle an error with different log levels
timeout(): Raise an exception if the function runs longer than the specified timeout
retry(): Retry a function when specific exceptions are raised, with configurable delay and max attempts
simple_cache(): Easy cache function with parameter caching method
abstract(): Mark a function as abstract, using LogLevels for error handling
deprecated(): Mark a function as deprecated, using LogLevels for warning handling
silent(): Make a function silent (disable stdout, and stderr if specified) (alternative to stouputils.ctx.Muffle)
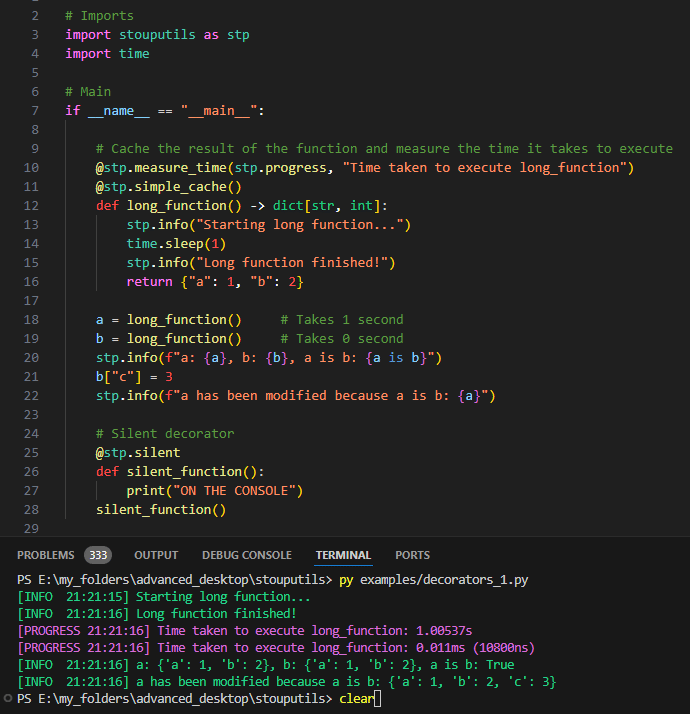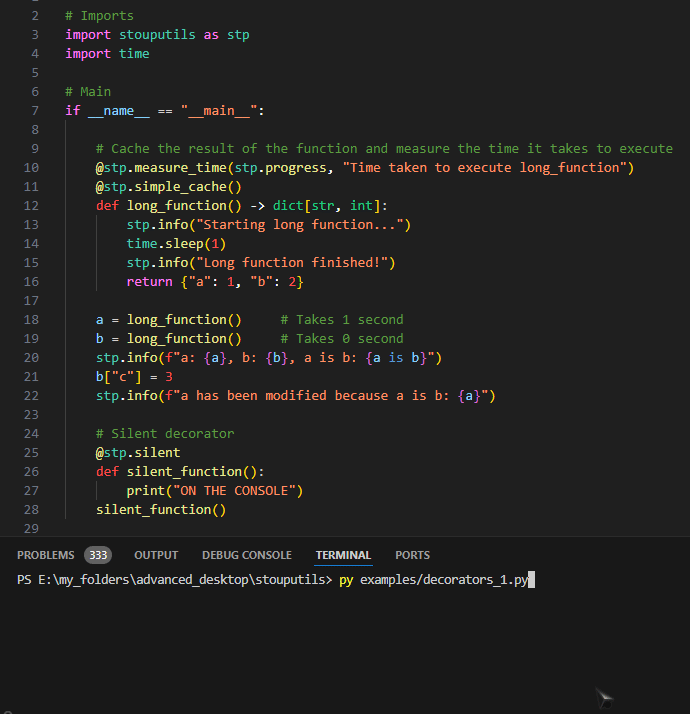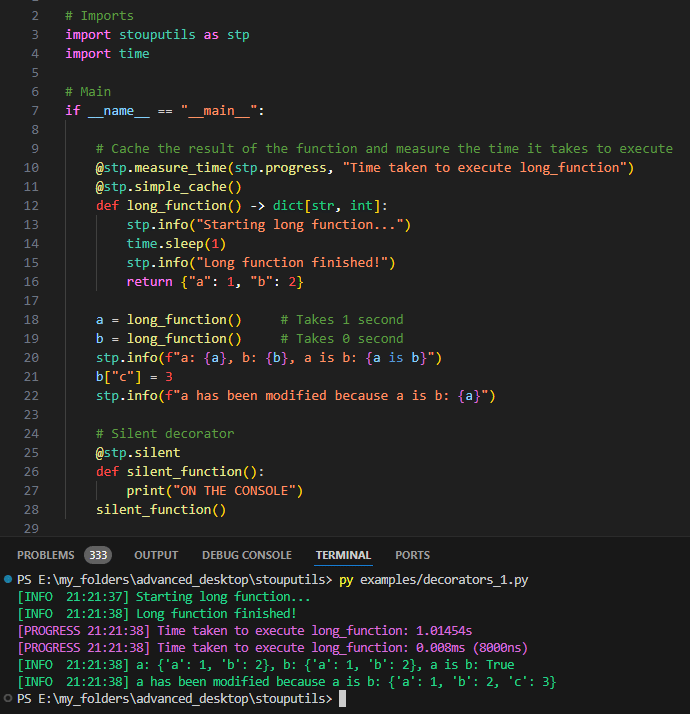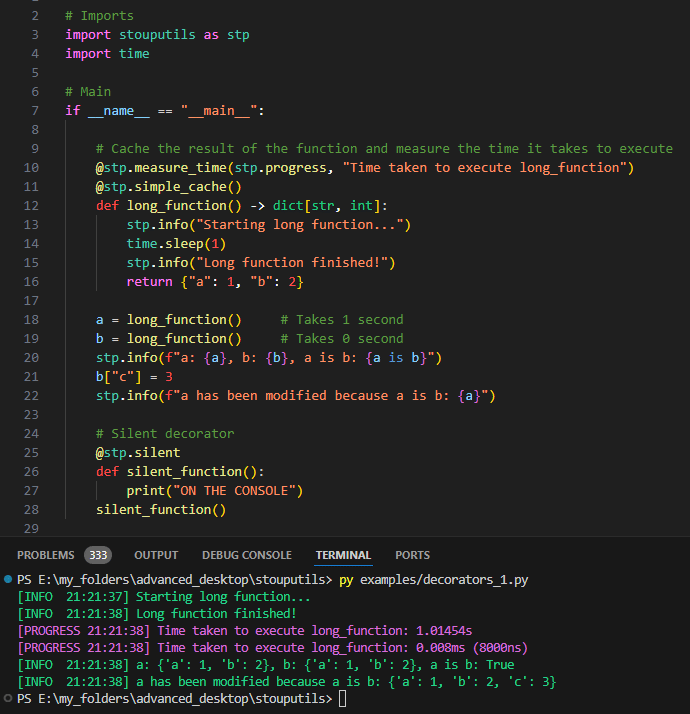
- measure_time(func: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~typing.Any] | None = None, *, printer: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], None] = <function progress>, message: str = '', perf_counter: bool = True, is_generator: bool = False) Callable[[...], Any][source]#
Decorator that will measure the execution time of a function and print it with the given print function
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to decorate
printer (Callable) – Function to use to print the execution time (e.g. debug, info, warning, error, etc.)
message (str) – Message to display with the execution time (e.g. “Execution time of Something”), defaults to “Execution time of {func.__name__}”
perf_counter (bool) – Whether to use time.perf_counter_ns or time.time_ns defaults to True (use time.perf_counter_ns)
is_generator (bool) – Whether the function is a generator or not (default: False) When True, the decorator will yield from the function instead of returning it.
- Returns:
Decorator to measure the time of the function.
- Return type:
Callable
Examples
> @measure_time(printer=info) > def test(): > pass > test() # [INFO HH:MM:SS] Execution time of test: 0.000ms (400ns)
- class LogLevels(*values)[source]#
Bases:
EnumLog level for the errors in the decorator handle_error()
- NONE = 0#
Do nothing
- WARNING = 1#
Show as warning
- WARNING_TRACEBACK = 2#
Show as warning with traceback
- ERROR_TRACEBACK = 3#
Show as error with traceback
- RAISE_EXCEPTION = 4#
Raise exception
- force_raise_exception: bool = False#
If true, error_log parameter will be set to RAISE_EXCEPTION for every next handle_error calls, useful for doctests
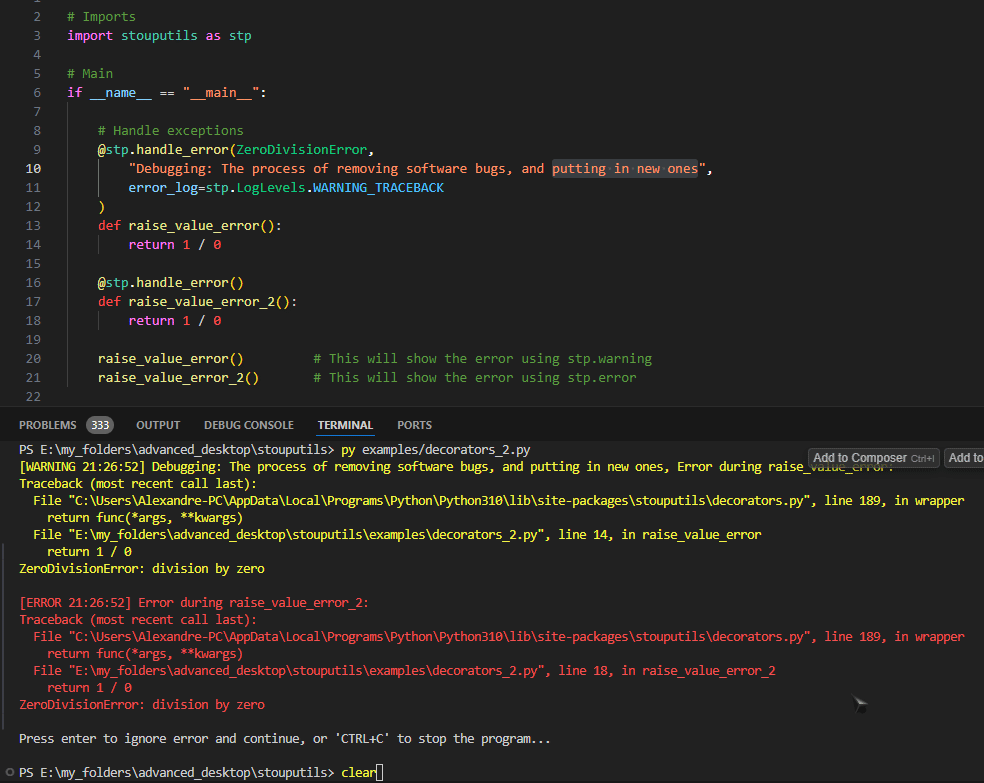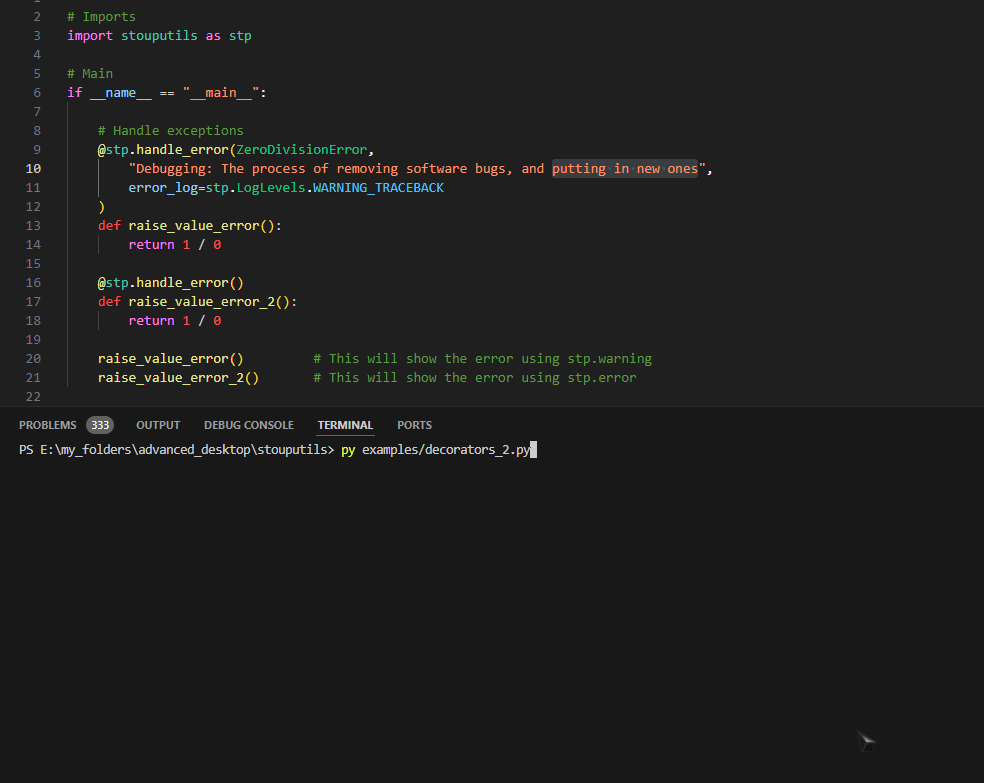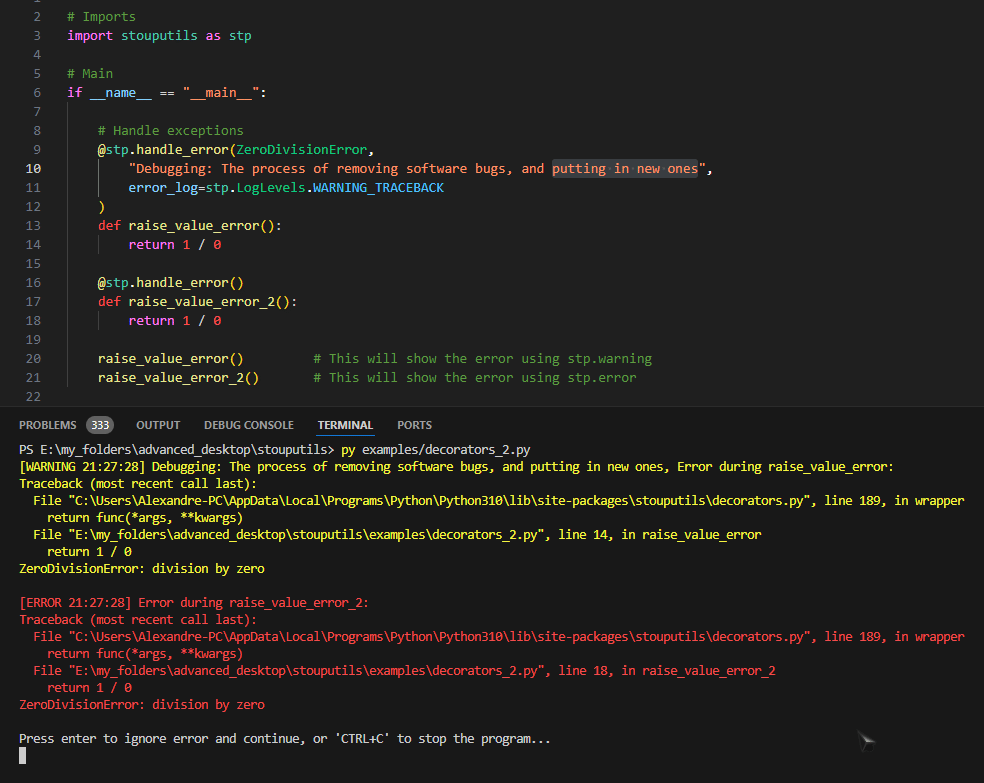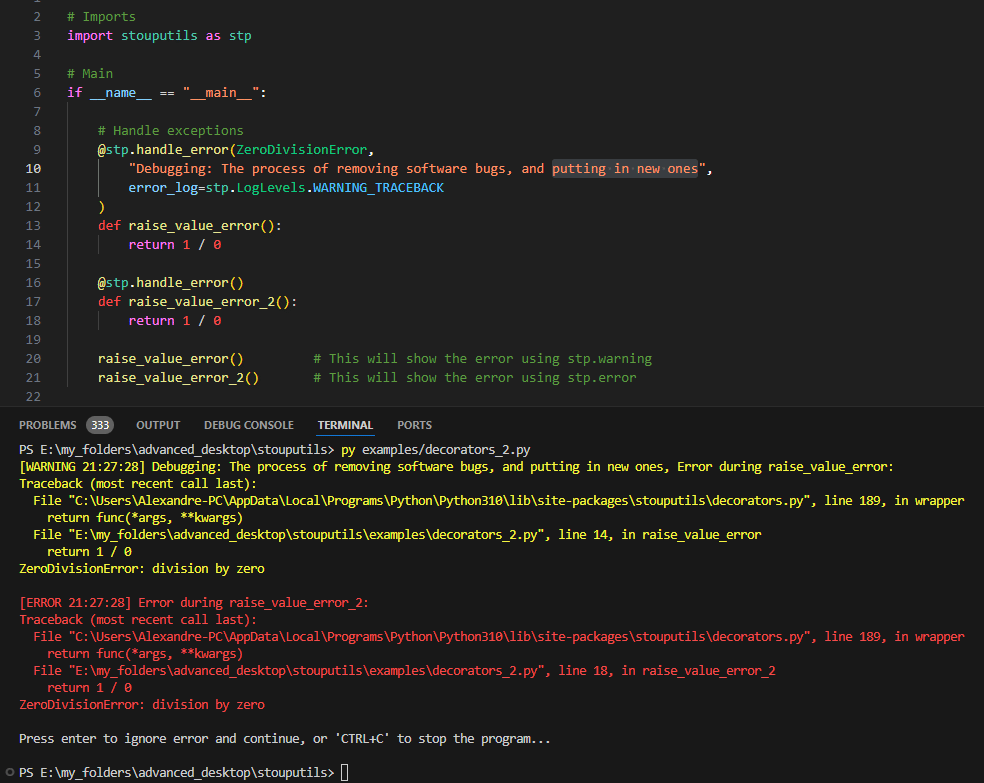
- handle_error(func: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~typing.Any] | None = None, *, exceptions: tuple[type[BaseException], ...] | type[BaseException] = (<class 'Exception'>,), message: str = '', error_log: ~stouputils.decorators.LogLevels = LogLevels.WARNING_TRACEBACK, sleep_time: float = 0.0) Callable[[...], Any][source]#
Decorator that handle an error with different log levels.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to decorate
exceptions (tuple[type[BaseException]], ...) – Exceptions to handle
message (str) – Message to display with the error. (e.g. “Error during something”)
error_log (LogLevels) – Log level for the errors LogLevels.NONE: None LogLevels.WARNING: Show as warning LogLevels.WARNING_TRACEBACK: Show as warning with traceback LogLevels.ERROR_TRACEBACK: Show as error with traceback LogLevels.RAISE_EXCEPTION: Raise exception
sleep_time (float) – Time to sleep after the error (e.g. 0.0 to not sleep, 1.0 to sleep for 1 second)
Examples
>>> @handle_error ... def might_fail(): ... raise ValueError("Let's fail")
>>> @handle_error(error_log=LogLevels.WARNING) ... def test(): ... raise ValueError("Let's fail") >>> # test() # [WARNING HH:MM:SS] Error during test: (ValueError) Let's fail
- timeout(
- func: Callable[[...], Any] | None = None,
- *,
- seconds: float = 60.0,
- message: str = '',
Decorator that raises a TimeoutError if the function runs longer than the specified timeout.
Note: This decorator uses SIGALRM on Unix systems, which only works in the main thread. On Windows or in non-main threads, it will fall back to a polling-based approach.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to apply timeout to
seconds (float) – Timeout duration in seconds (default: 60.0)
message (str) – Custom timeout message (default: “Function ‘{func_name}’ timed out after {seconds} seconds”)
- Returns:
Decorator that enforces timeout on the function
- Return type:
Callable[…, Any]
- Raises:
TimeoutError – If the function execution exceeds the timeout duration
Examples
>>> @timeout(seconds=2.0) ... def slow_function(): ... time.sleep(5) >>> slow_function() # Raises TimeoutError after 2 seconds Traceback (most recent call last): ... TimeoutError: Function 'slow_function()' timed out after 2.0 seconds
>>> @timeout(seconds=1.0, message="Custom timeout message") ... def another_slow_function(): ... time.sleep(3) >>> another_slow_function() # Raises TimeoutError after 1 second Traceback (most recent call last): ... TimeoutError: Custom timeout message
- retry(func: ~collections.abc.Callable[[...], ~typing.Any] | None = None, *, exceptions: tuple[type[BaseException], ...] | type[BaseException] = (<class 'Exception'>,), max_attempts: int = 10, delay: float = 1.0, backoff: float = 1.0, message: str = '') Callable[[...], Any][source]#
Decorator that retries a function when specific exceptions are raised.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to retry
exceptions (tuple[type[BaseException], ...]) – Exceptions to catch and retry on
max_attempts (int | None) – Maximum number of attempts (None for infinite retries)
delay (float) – Initial delay in seconds between retries (default: 1.0)
backoff (float) – Multiplier for delay after each retry (default: 1.0 for constant delay)
message (str) – Custom message to display before “, retrying” (default: “{ExceptionName} encountered while running {func_name}”)
- Returns:
Decorator that retries the function on specified exceptions
- Return type:
Callable[…, Any]
Examples
>>> import os >>> @retry(exceptions=PermissionError, max_attempts=3, delay=0.1) ... def write_file(): ... with open("test.txt", "w") as f: ... f.write("test")
>>> @retry(exceptions=(OSError, IOError), delay=0.5, backoff=2.0) ... def network_call(): ... pass
>>> @retry(max_attempts=5, delay=1.0) ... def might_fail(): ... pass
- simple_cache(
- func: Callable[[...], Any] | None = None,
- *,
- method: Literal['str', 'pickle'] = 'str',
Decorator that caches the result of a function based on its arguments.
The str method is often faster than the pickle method (by a little) but not as accurate with complex objects.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to cache
method (Literal["str", "pickle"]) – The method to use for caching.
- Returns:
A decorator that caches the result of a function.
- Return type:
Callable[…, Any]
Examples
>>> @simple_cache ... def test1(a: int, b: int) -> int: ... return a + b
>>> @simple_cache(method="str") ... def test2(a: int, b: int) -> int: ... return a + b >>> test2(1, 2) 3 >>> test2(1, 2) 3 >>> test2(3, 4) 7
>>> @simple_cache ... def factorial(n: int) -> int: ... return n * factorial(n - 1) if n else 1 >>> factorial(10) # no previously cached result, makes 11 recursive calls 3628800 >>> factorial(5) # no new calls, just returns the cached result 120 >>> factorial(12) # two new recursive calls, factorial(10) is cached 479001600
- abstract(
- func: Callable[[...], Any] | None = None,
- *,
- error_log: LogLevels = LogLevels.RAISE_EXCEPTION,
Decorator that marks a function as abstract.
Contrary to the abstractmethod decorator from the abc module that raises a TypeError when you try to instantiate a class that has abstract methods, this decorator raises a NotImplementedError ONLY when the decorated function is called, indicating that the function must be implemented by a subclass.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – The function to mark as abstract
error_log (LogLevels) – Log level for the error handling LogLevels.NONE: None LogLevels.WARNING: Show as warning LogLevels.WARNING_TRACEBACK: Show as warning with traceback LogLevels.ERROR_TRACEBACK: Show as error with traceback LogLevels.RAISE_EXCEPTION: Raise exception
- Returns:
Decorator that raises NotImplementedError when called
- Return type:
Callable[…, Any]
Examples
>>> class Base: ... @abstract ... def method(self): ... pass >>> Base().method() Traceback (most recent call last): ... NotImplementedError: Function 'method()' is abstract and must be implemented by a subclass
- deprecated(
- func: Callable[[...], Any] | None = None,
- *,
- message: str = '',
- version: str = '',
- error_log: LogLevels = LogLevels.WARNING,
Decorator that marks a function as deprecated.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to mark as deprecated
message (str) – Additional message to display with the deprecation warning
version (str) – Version since when the function is deprecated (e.g. “v1.2.0”)
error_log (LogLevels) – Log level for the deprecation warning LogLevels.NONE: None LogLevels.WARNING: Show as warning LogLevels.WARNING_TRACEBACK: Show as warning with traceback LogLevels.ERROR_TRACEBACK: Show as error with traceback LogLevels.RAISE_EXCEPTION: Raise exception
- Returns:
Decorator that marks a function as deprecated
- Return type:
Callable[…, Any]
Examples
>>> @deprecated ... def old_function(): ... pass
>>> @deprecated(message="Use 'new_function()' instead", error_log=LogLevels.WARNING) ... def another_old_function(): ... pass
- silent(
- func: Callable[[...], Any] | None = None,
- *,
- mute_stderr: bool = False,
Decorator that makes a function silent (disable stdout, and stderr if specified).
Alternative to stouputils.ctx.Muffle.
- Parameters:
func (Callable[..., Any] | None) – Function to make silent
mute_stderr (bool) – Whether to mute stderr or not
Examples
>>> @silent ... def test(): ... print("Hello, world!") >>> test()
>>> @silent(mute_stderr=True) ... def test2(): ... print("Hello, world!") >>> test2()
>>> silent(print)("Hello, world!")
- _get_func_name(
- func: Callable[[...], Any],
Get the name of a function, returns “<unknown>” if the name cannot be retrieved.
- _get_wrapper_name(
- decorator_name: str,
- func: Callable[[...], Any],
Get a descriptive name for a wrapper function.
- Parameters:
decorator_name (str) – Name of the decorator
func (Callable[..., Any]) – Function being decorated
- Returns:
Combined name for the wrapper function (e.g., “stouputils.decorators.handle_error@function_name”)
- Return type:
str